Cosmetics industry
Cosmetics industry
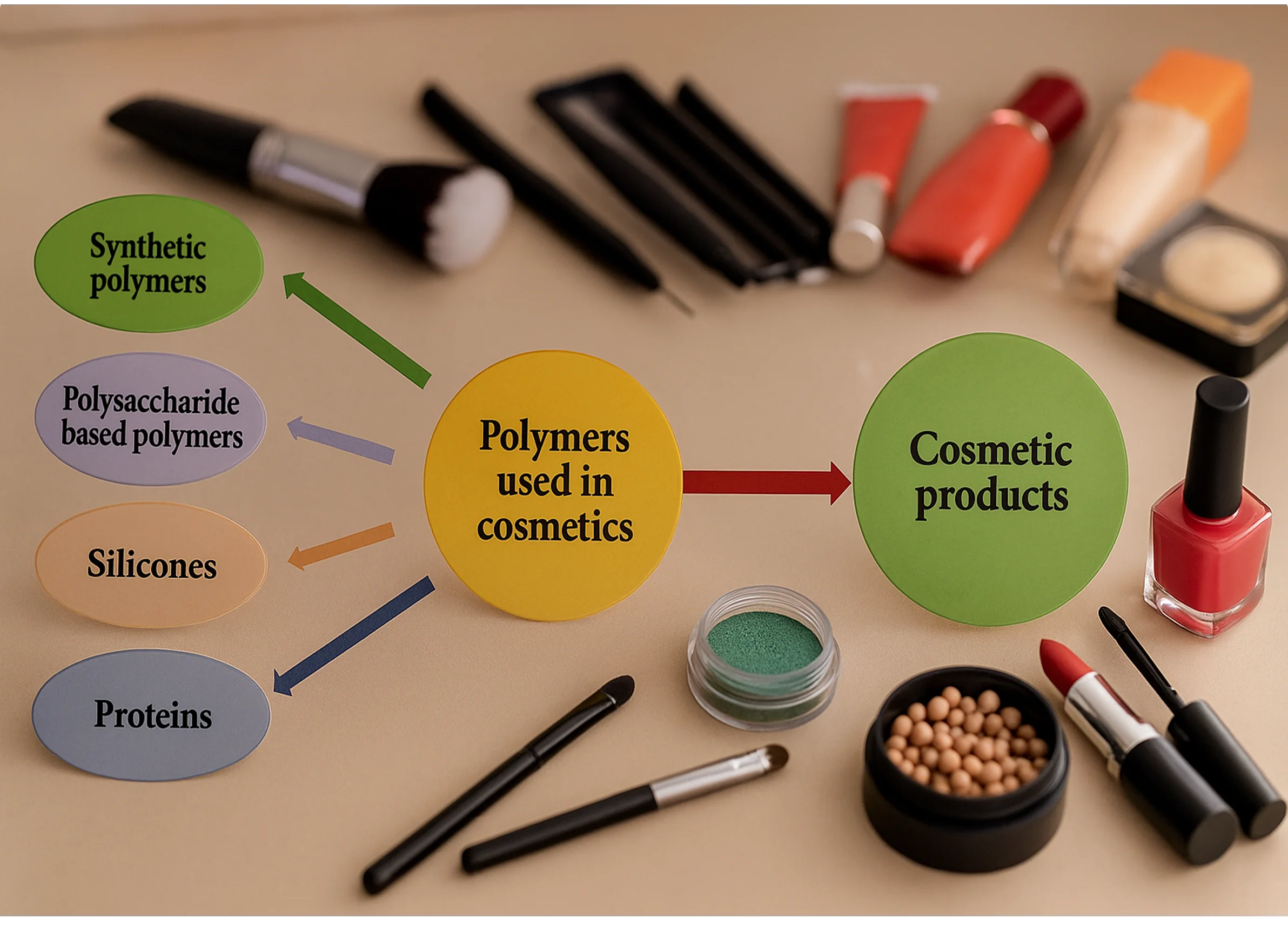
Cosmetic products are designed to enhance beauty, cleanse, and alter the appearance of the human body. Polymers play various roles in cosmetic formulations, including acting as rheology modifiers, emulsifiers, emollients, film formers, and antimicrobial agents. These polymers can be classified into four main types:
Ingredients
When discussing cosmetic ingredients, they can be divided into three main groups based on their roles. Functional ingredients, which directly affect the effectiveness of cosmetic products, include polymers, surfactants, emollients, humectants, pigments, and active ingredients.
Functional ingredients
These are the main ingredients that provide consumers with the main benefits, such as cleansing, moisturizing or emollient. They contain active ingredients that enhance the effectiveness of products, including over-the-counter (OTC) drugs.
Ingredients of aesthetics
These materials improve the look and feel of the product and enhance the overall user experience. They address issues such as the texture and smell of the product and make it more pleasant to use.
Providing general and specialized equipment
Although these ingredients have little effect on product performance, they support the marketing narrative and influence consumer preferences. For example, consumers may prefer a product to the more effective Petroatom due to the presence of Aloe Vera.
thickeners
Polymers create gels by increasing the viscosity of aqueous formulations. Natural thickeners such as starch and xanthan gum and synthetic types such as polyacrylates are used. Innovations include advanced copolymers and thermosensitive systems.
Hair products
Cationic polymers are effective in hair care due to the negative charge of the hair. Natural options include polysaccharides and hydrolyzed proteins, and synthetic polymers such as polyvinylpyrrolidone and silicones are also used.
Structural factors
These substances create hardness and include waxes, lanolin, and long-chain fatty alcohols. Polyalphaolefin is used in eye shadow, glycol stearate for a pearl effect, and polyurethanes in mascara and nail products.
Delivery systems
Polymers can encapsulate active ingredients and improve their stability and release, and can carry both natural antioxidants (such as vitamins C and E) and synthetic compounds.
Cosmetics industry

Surfactants
Surfactants are essential ingredients in cosmetic products that can form structures such as micelles in water due to their compatibility with water and oil. Their key functions in cosmetic products include the following:
wetting
Surfactants reduce the contact angle between solutions and surfaces and increase their ability to spread and penetrate fat deposits. This feature helps to improve the removal of fats and increase the spreadability of creams and lotions
cleaning
Surfactants help to clean the skin and hair and remove solid particles and fat residues. Their lipophilic ends absorb fats while their hydrophilic ends interact with fat deposits and facilitate their removal during washing.
Foam
Surfactants stabilize air bubbles in cleaning products and create foam. Although foam does not significantly help in removing dirt, it is a desirable feature for consumers and helps to make the product attractive.
thickening
In water-based solutions, surfactants form micelles that affect viscosity. The packing of the micelles can be altered by the addition of salt, thus creating more concentrated detergent formulations.
Emulsification
Surfactants are essential for creating stable oil-water mixtures (emulsions) that form the basis of creams and lotions. These emulsions can be simple or complex and each one has specific purposes in makeup.

Interactions between surfactants and polymers
Polymers in cosmetic products are influenced by interactions with surfactants that help break down fatty substances. These surfactants are classified based on the charge of hydrophilic groups.
Surfactant chain length
For uncharged polymers, the binding concentration of ionic surfactants in a homogeneous series decreases with increasing surfactant chain length.
Surfactant structure
The type of head group in the surfactant plays an important role in its interactions with uncharged or water-soluble polymers. Nonionic surfactants do not react with simple uncharged polymers, while anionic surfactants react strongly with cationic polymers but weakly or nonreactive with anionic polymers.
Polymer properties
(a) Polymer weight: A minimum polymer weight is required for interactions to occur. For example, hydrophobically modified polymers need a molecular weight about 1000 times greater to effectively interact with caffeine and nonionic surfactants.
(b) Polymer amount: The amounts of polymer and surfactant must be equal for effective interactions to take place.
(c) Polymer structure: There are significant differences in the reactivity of various polymers and surfactants. For effective interactions between ionic surfactants and uncharged polymers, there must be distinct differences in their reactivity.
(d) Added salts: The presence of salts can influence the interactions between ionic surfactants and polymers.
Types of surfactants
Surfactants can be classified based on their counterion charge or their ability to form ions in solution. Their four main types include anionic, amphoteric, cationic and non-ionic surfactants, each of which has different purposes in cosmetic products.
Anionic surfactants
Negatively charged surfactants such as sodium and ammonium lauryl sulfate are used in cleaning products due to their ability to remove grease and dirt and produce a lot of foam.
Amphoteric surfactants
Positively or negatively charged zwitterionic surfactants are valuable due to effective cleaning, less irritation and improved foam quality.
Nonionic surfactants
These uncharged surfactants, such as fatty alcohols and amine oxides, do not decompose in water and are not affected by salt.
Cationic surfactants
Positively charged surfactants are less cleansing and more effective in hair conditioners, but are incompatible with anionic surfactants.
Applications of polymeric surfactants
Traditional surfactants are low molecular weight materials, usually in the hundreds.

Block and graft polymer surfactants are very valuable in the pharmaceutical industry due to their superior surface activity and are used as drug carriers, emulsifiers, dispersing agents, wetting agents, phase transfer catalysts in the synthesis and analysis of drugs.

The presence of solid paraffin in extracted crude oil leads to poor fluidity and creates challenges in the production, storage and processing of this highly viscous and easily gelled substance.

In the textile printing and dyeing sector, polyether-type polymeric surfactants are widely used as low-foam detergents, emulsifiers, dispersants, antifoams, antistatic agents, wetting agents, and dyeing agents.

High molecular weight surfactants play a vital role in improving paper performance and increasing the efficiency of papermaking machines, which has led to an increase in the interest of professionals in the papermaking industry..

Colorants are vital components in various cosmetic products, especially in color makeup. The majority of cosmetic pigments are synthetic and are subject to international regulations.

Cosmetic active ingredients are chemical compounds present in cosmetic products that provide specific functions and effects. These ingredients can help repair, protect, nourish and heal the skin and help with beauty, anti-aging and skin care..
