Base oils
- Home
- >
- Hydrocarbon derivatives
- >
- base oil
Hydrocarbon Derivatives
Base oils
Base oils play an essential role in lubricant production, and among the various options, Base Oil is notable for its distinctive features and advantages.

Group I
Group I base oils are the most widely used and least expensive type of base oil. They are produced from crude oil that has been refined to remove impurities and improve its performance characteristics. Group I base oils have a relatively low viscosity index (VI) and are typically used in low-performance.
Group II
These oils are typically produced through the hydrocracking process, which is more complex than the method used for producing Group I base oils. Due to the saturation of all hydrocarbon molecules in these oils, Group II base oils possess better antioxidant properties. Additionally, these oils have a lighter color and are priced higher compared to Group I base oils.
Group III
Group III base oils are premium, highly refined mineral oils known for their superior performance characteristics, such as a high viscosity index and excellent thermal stability. they provide improved fuel economy and enhanced engine protection. Their exceptional qualities result from extensive refining and processing of high-quality crude oil.
Group IV
Group IV base oils are synthetic polyalphaolefin (PAO) oils that have been in use for over 50 years. Unlike previous groups, which are derived from the distillation and refining of crude oil, PAOs are produced as pure chemicals in a chemical plant. Classified as synthetic hydrocarbons (SHCs), they boast a viscosity index (VI) exceeding 120 (dl/g) and are considerably more expensive than Group III base oils due to the extensive processing required for their production.
Group V
Group V base oils encompass all base oils that are not categorized within Groups I, II, III, or IV. This includes naphthenic base oils, various synthetic esters, polyalkylene glycols (PAGs), phosphate esters, and other similar oils.
Hydrocarbon Derivatives
Types of Base Oil
Base oils are generally divided into two main categories: mineral base oils and synthetic base oils, which include Group I and Group II/III. This classification is determined by the level of refinement and processing that the base oil has undergone.
| Group V | Group IV | Group III | Group II | Group I | Types of Base Oil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| includes all synthetic fluids other than PAOs | PAOs synthetic lubricant | >120 | 80-120 | 80-120 | VI (dl/g) |
| All other base oils not included in groups I, II, III, or IV | PAOs synthetic lubricant | <0.03 | <0.03 | >0.03 | Sulfur (%) |
| All other base oils not included in groups I, II, III, or IV | PAOs synthetic lubricant | >90 | >90 | <90 | saturates(%) |
| Bio degradable base and food grade lubricants | Is the presence of (PAOs) as a new element | including aerospace lubricants, industrial lubricants, and high-performance automotive engine oils | Automotive engine oils, Industrial lubricants, Compressor oilsا | applications, including: Automotive engine oils, Industrial lubricants, Greases | Applications |
Hydrocarbon Derivatives
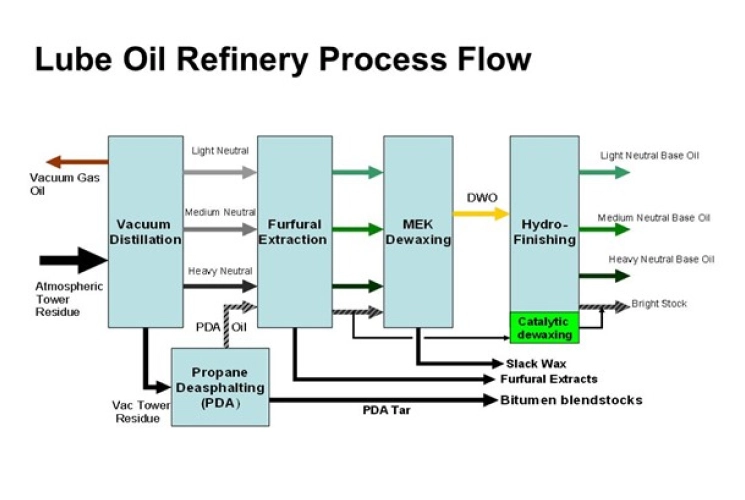
Mineral Base Oil Production Process
Nearly all lubricants utilized in industrial settings today originated as base oil. The base oil classification outlines the composition of the oil, its manufacturing process, and its performance in various conditions, including extreme temperatures.
| Property method | Crucial reason | Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | Specifies the viscosity grade of base oil. | Viscometer |
| Viscosity index | Describes the relationship between viscosity and temperature. | Viscosity difference between 40°C and 100°C, indexed. |
| Specific gravity | Specifies the density of oil in comparison to water. | Specific gravity meter |
| Flash point | Explains the characteristics of high-temperature volatility and flammability. | Flash point tester, the temperature at which a surface flame is produced. |
| Pour point | Describes the fluidity behavior of oil at low temperatures. | Gravity flow in a testing jar, temperature |
Physical Characteristics of Base Stocks
